Table of Contents
What are Ghosting and Burn-in? - Learn How to Care for Your Monitors and Screens

It is not uncommon to experience problems with our monitors with prolonged usage. Over time, we may experience faint stationary images, logos or text that seem stuck on our screens even when we constantly switch between different screen images.
This issue is known as image retention or burn-in. On the other hand, when our monitor’s refresh rates and response time are incompatible with games or content that require high frame rates or frames per second (FPS), we may experience ghosting.
In this article, we will explain what is ghosting and burn-in, how to prevent them from occurring and how to address them.
What is Ghosting?
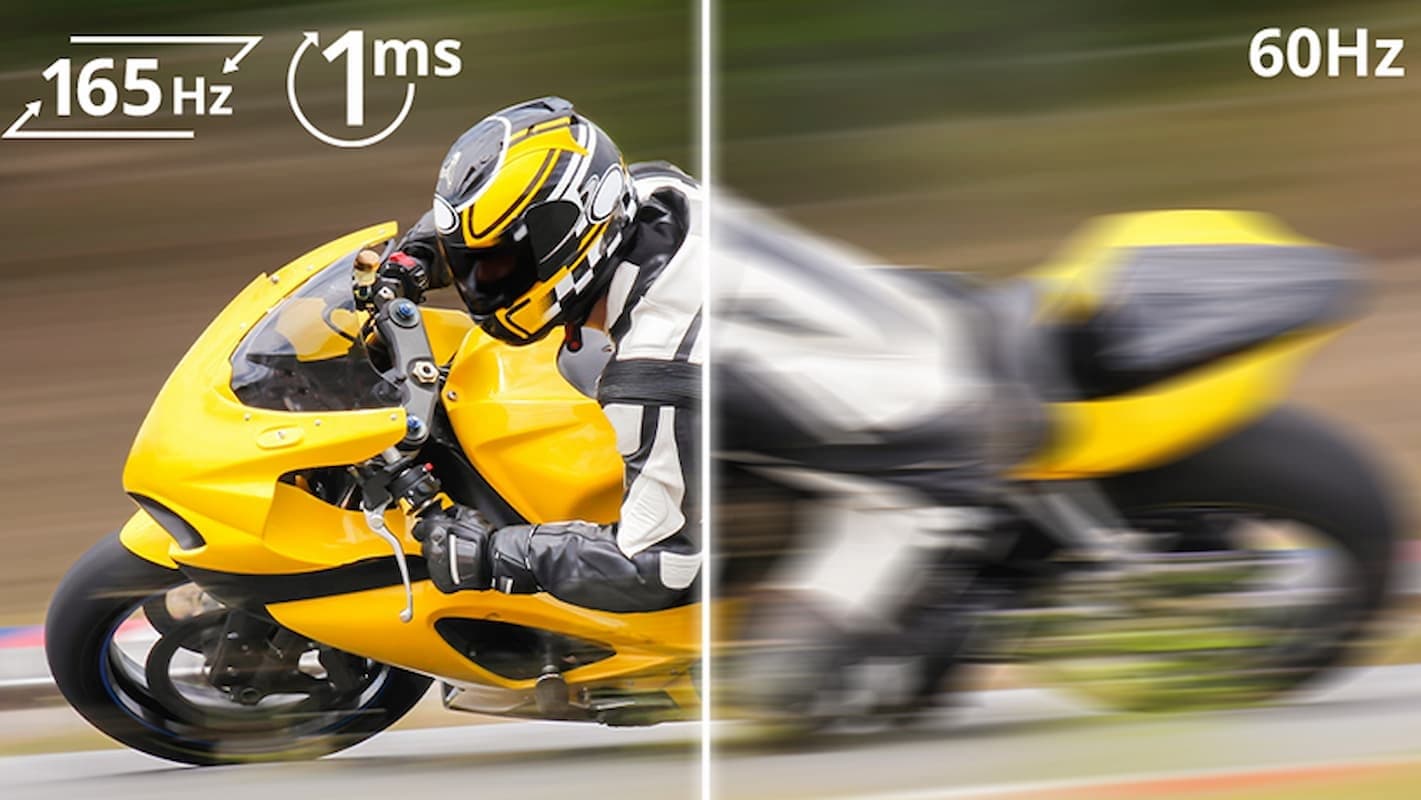
Ghosting refers to the lingering trail of an image previously displayed on a screen. Its appearance resembles that of faint, blurry and temporary afterimages following fast-moving objects on a screen. It occurs when the pixels are not able to change from one colour to another fast enough and consequently, results in the ghosting effect.

Example of Ghosting from Blur Busters
Causes of Ghosting
Ghosting can be the result of the monitor’s slow pixel response time relative to the requirements of fast-paced games or content, resulting in a slight delay in the image changes on screen.
Secondly, faulty monitor components can also result in ghosting. This includes frayed cables, damaged devices connected to the monitor, or even the video ports on the monitor itself. Damaged components could lead to overheating and potentially affect the response time and refresh rate of the monitor.
Solution(s) for Ghosting
Before attempting to fix any perceived ghosting issue, one can utilise the free online Blur Busters Motion Test to assess the extent of the ghosting problem. A green “Ready” signal means that the test is ready for evaluation and observation.

Recorded Video from Blur Busters Motion Test
If you can observe the moving UFOs without significant blurring or faint trails, then that indicates good motion handling.
However, if you do observe significant blurring of trails, then that indicates ghosting. The severity of the ghosting problem varies depending on the monitor and other factors.
The first solution is to adjust the overdrive settings. This can be found on the on-screen display settings of monitors. “Overdrive” may have alternative terms like “motion acceleration” and “trace free” depending on the manufacturer of the monitor.
The overdrive feature of modern monitors serves to increase the pixel response time by increasing the voltage to liquid crystals in the display, enabling the pixels to change colour more rapidly. This helps to address ghosting issues.
However, if the overdrive settings are calibrated incorrectly or set too fast for the pixels, this can cause inverse ghosting or pixel overshoot where the pixels overshoot their targeted colour brightness level before trying to correct themselves again. This results in the temporary trails observed. Hence, overdrive requires careful calibration.

Example of Inverse Ghosting from Blur Busters
Lastly, if faulty devices and monitor components are the issues, aim to get them replaced and check your monitor’s warranty policy to see if you can consult a professional for advice and assessment.
PRISM+ Warranty Policy:
| Product | Warranty Duration | Warranty Type | Scope of Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitors | 3 years | On-site | Labour, parts & transport |
| Portable Monitors | 1 year | On-site | Labour, parts & transport |
For more details on PRISM+ Warranty Policy, click here.
[Note: No registration is required to qualify for the PRISM+ warranty. However, it is recommended that customers keep a copy of their invoice and take note of their order number should the need for a warranty claim ever arise.]
What is Burn-in?
Burn-in refers to a more permanent and severe form of image retention where the screen retains faint static images even after transitioning from one image to another.
This occurs when the screen remains static for a long period of time, resulting in some pixels “burning-in” as they have been emitting light for too long. This causes degradation and subsequently, the pixels are not able to return to their normal state.
Image retention, on the other hand, is less severe, usually temporary and easier to fix.

Causes of Burn-in
Some common static images like company logos, time displays and backgrounds tend to remain in the same position on the screen for long periods. This results in the pixels forming these images to burn-in.
To prevent image retention or burn-in, here are some good practices to follow:
- Turn off display screens when not in use.
- Avoid leaving a video paused or an image retained for long periods. While there is no specific time limit that guarantees burn-in will not occur, the general guideline is to avoid displaying static images on screen for more than a few hours. For OLED displays, it is good practice to avoid displaying static content exceeding 1-2 hours.
- Reduce the brightness levels and contrast ratio to reduce stress on the pixels.
- Utilise dynamic screen-saver features to automatically reduce the brightness of the screen and put your monitor to sleep mode when not in use.
Solution(s) for Burn-in
There is no perfect cure for severe image retention. However, one can reduce the visibility of image retention and avoid further pixel degradation.
Check if your monitor has any screen maintenance or pixel refresher features and utilise them.
These features can recalibrate pixel brightness values and alleviate some image retention.
If your monitor does not possess such features, there are applications and online tools that deal with screen burn-in problems. These applications include ScreenBurnFixer and JScreenFix which display dynamic colour patterns and rapid pixel change to balance the pixel degradation and reduce the visibility of burn-in effects.

Screenshot of JScreenFix.
In conclusion, burn-in is not limited only to monitors. It’s also common in smartphones, televisions, tablets and smartwatches.
That being said, some extent of screen degradation due to prolonged years of use may be unavoidable. However, the solutions in this article can help you to address some of the problems faced like ghosting and burn-in, and extend the lifespan of your monitor.
FAQs
|
Can ghosting and burn-in occur on all types of monitors? Yes, ghosting and burn-in can occur on various monitor technologies, but some types, like OLED, are more prone to burn-in. Do all monitors have adjustable response times? No, not all monitors have adjustable response times. It is advisable to check the specifications before purchasing to ensure the desired response time. Can burn-in be completely reversed once it occurs? Burn-in is generally considered permanent, and complete reversal may not be possible. However, preventive measures can minimize its occurrence. Is ghosting only noticeable during fast-paced content, such as gaming? Ghosting can be noticeable during fast-paced content, but it may also manifest during regular usage when the monitor's response time is slow. How often should I update my graphics card drivers? It is recommended to update your graphics card drivers regularly, as new updates often include optimizations and bug fixes that can improve overall performance. |